We take a closer look at the nuances of intermittent fasting.
What is it? A meal pattern based on specific start and end times.
What is liquid-focused nutrition? Consuming ample water and, if possible, other zero-calorie beverages, such as herbal tea or black coffee.
“Research has shown a strong correlation between fasting and increased lifespan.”
Defining Fasting: What Counts and What Doesn’t
Fasting Is:
Time-Bound: Having specific start and end times, whether it’s hours or days.
Fluid-Intensive: Drinking plenty of water and possibly other zero-calorie beverages like herbal tea or black coffee.
Fasting Is Not:
Starvation: Fasting is a controlled and voluntary practice, while starvation is forced and harmful.
Dehydration: Water intake is crucial during fasting; neglecting hydration can lead to serious health issues.
Tools and Guidelines for Effective Fasting
Start Gradually: If you’re new to fasting, begin with shorter periods and gradually increase as your body adapts.
Use Fasting Apps: Apps like ‘Zero’ can help track your fasting periods, ensuring you stay on schedule.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and aid in toxin removal.
Break Your Fast Gently: Start with light, easily digestible foods like fruits, vegetables, or broths.
Fasting and Longevity: A Symbiotic Relationship
Research has shown a strong correlation between fasting and increased lifespan. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, enhancing cellular repair processes, and promoting autophagy (the body’s way of cleaning out damaged cells), fasting contributes to a healthier, longer life. Moreover, it encourages metabolic efficiency, teaching the body to use its energy resources more effectively.
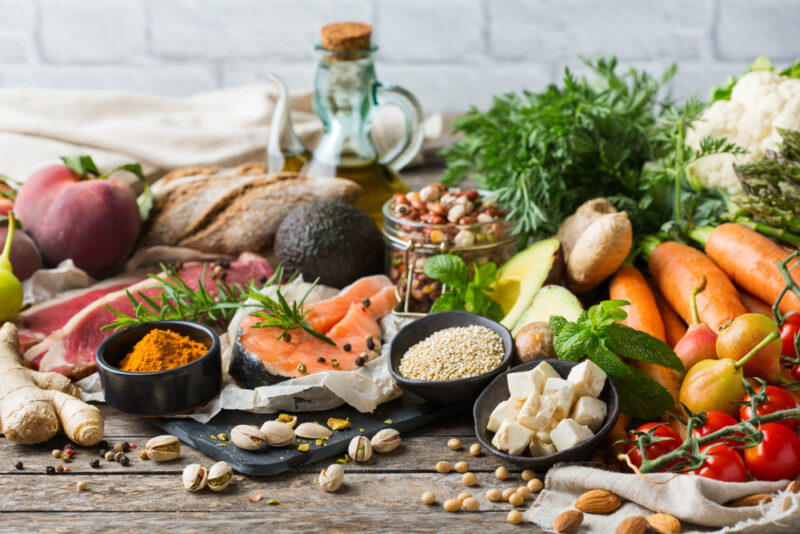

Food Choices for Longevity and Effective Fasting
During Eating Windows:
Opt for Whole Foods: Choose fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Include Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
Stay Balanced: Ensure a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients.
Post-Fasting:
Reintroduce Foods Slowly: Start with easily digestible foods, progressively reintroducing more complex foods.
Monitor Portion Sizes: Avoid overeating immediately after a fast to prevent digestive discomfort.
Foods to Promote Longevity:
Berries and Leafy Greens: Rich in antioxidants, they combat oxidative stress.
Nuts and Seeds: Provide healthy fats, proteins, and a range of nutrients.
Legumes: A great source of fiber, protein, and essential nutrients.
Harmonising Fasting, Longevity, and Nutrition
Fasting stands as a multifaceted health practice, capable of enhancing both physical and mental well-being, while also showing promising connections with increased lifespan. By following clear guidelines, ensuring proper hydration, and making thoughtful food choices, individuals can harness the full spectrum of benefits that fasting has to offer, paving the way for a healthier, more vibrant life.
Remember, it’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before embarking on any fasting regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or specific nutritional needs. Through a balanced and mindful approach, fasting can become a powerful tool in your wellness arsenal, promoting longevity and optimal health.