It’s as crucial to our health as eating a balanced diet and staying physically active. Sleep provides our bodies and minds with the essential time to rejuvenate, repair, and recharge. Neglecting it can have profound consequences, impacting not only our physical health but also our mental well-being.
What happens when you don’t get enough sleep? The repercussions of sleep deprivation are far-reaching, affecting various aspects of our lives:
Physical Problems
Sleep provides our bodies and minds with the opportunity to rejuvenate, repair, and recharge. Neglecting the importance of sleep can lead to profound consequences that impact not only our physical but also our mental health.
Fatigue: Sleep-deprived individuals often battle persistent fatigue, making it difficult to stay alert and focused during the day.
Cognitive Impairment: Lack of sleep can impair memory and cognitive functions, hindering our ability to think clearly and make sound decisions.
Increased Accident Risk: Sleep-deprived individuals are at a higher risk of accidents and injuries due to reduced alertness.
Weakened Immune System: Quality sleep plays a pivotal role in maintaining a robust immune system. Sleep deprivation can make us more susceptible to illnesses.
Chronic Disease Risk: Long-term sleep problems have been linked to a heightened risk of chronic conditions like heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and obesity.
“Regular exercise can enhance sleep quality, but avoid vigorous workouts too close to bedtime, as they can make falling asleep challenging.”
Mental Health Issues
Irritability: A lack of sleep can lead to heightened irritability and mood swings.
Anxiety and Depression: Sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of anxiety and depression.
Stress Management: Sleep is crucial for managing stress effectively.
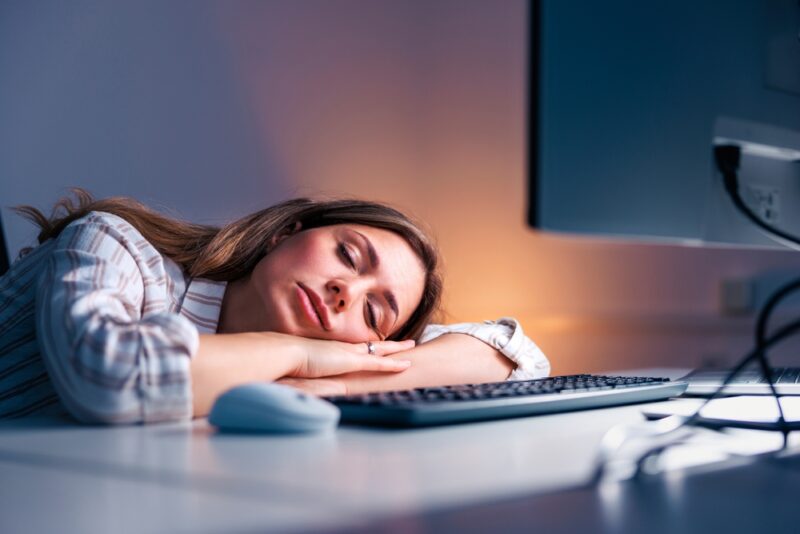

The Importance of Sleep Hygiene
To unlock the full potential of sleep, it’s essential to practice good sleep hygiene. Here are some valuable tips to help you achieve optimal sleep quality and duration:
Consistent Sleep Schedule: Set a regular sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same times daily, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Create a calming bedtime routine that prepares your body and mind for sleep. This could include activities like taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to soothing music. Avoid stimulating activities like watching TV or using electronic devices, as the blue light emitted can interfere with sleep.
Ideal Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Darkness promotes the production of melatonin, a hormone crucial for sleep regulation. Noise and light disruptions should be minimized, and maintaining a cool temperature is optimal for quality sleep.
Mindful Consumption: Avoid consuming caffeine and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime, as both can disrupt your sleep patterns.
Exercise Wisely: Regular exercise can enhance sleep quality, but avoid vigorous workouts too close to bedtime, as they can make falling asleep challenging.
Seek Professional Help for Chronic Insomnia: If you constantly struggle with falling asleep or staying asleep, consider consulting a healthcare professional, as there might be underlying medical issues affecting your sleep.
Circadian Rhythm: Your Internal Sleep-Wake Clock
Our internal sleep-wake cycle, known as the circadian rhythm, is regulated by a master clock located in the hypothalamus of the brain. This rhythm is influenced by external factors, including exposure to light and darkness, meal times, and physical activity. When our circadian rhythm is in harmony with our environment, we are more likely to achieve restorative sleep.
One effective way to align your circadian rhythm is to expose yourself to bright light during the day and minimize exposure to light, especially blue light from electronic devices, at night. Blue light suppresses the production of melatonin, making it harder to fall asleep. Consider using blue light filters or wearing blue light-blocking glasses if you must use screens before bedtime.
The Role of Body Temperature
Body temperature plays a pivotal role in regulating sleep. As evening approaches, our body temperature naturally drops, signaling the body that it’s time to prepare for sleep. Maintaining an optimal sleep environment, such as a cool bedroom, can aid in facilitating this temperature drop. Additionally, a warm bath before bed can help raise your body temperature slightly, promoting relaxation and aiding the subsequent temperature drop conducive to sleep.
Maximizing Your Sleep for Longevity and Biohacking
Good sleep isn’t just about feeling refreshed in the morning; it’s a powerful tool for enhancing longevity and optimizing your biohacking potential. Here are additional tips to boost the benefits of your slumber:
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Avoid heavy meals and sugary snacks before bedtime.
Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.
Prioritize Exercise: Regular physical activity contributes to better sleep quality.
Expose Yourself to Daylight: Natural light exposure during the day helps regulate your circadian rhythm.
Consistent Sleep Duration: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
In conclusion, sleep is the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, longevity, and biohacking. By adhering to these tips and making sleep a priority in your life, you can unlock its tremendous benefits for your body, mind, and overall well-being. Sweet dreams, and here’s to a healthier, more vibrant you!
Guarding Against EMF Radiation
In our modern world, we’re surrounded by electronic devices emitting electromagnetic fields (EMF) radiation, which can interfere with our sleep. To minimize EMF radiation exposure:
-Turn off all electronic devices in your bedroom.
-Relocate your bed away from electrical outlets and power lines.